Stablecoins have become integral to the cryptocurrency ecosystem, offering a bridge between volatile digital assets and traditional fiat currencies. Major stablecoins like Tether (USDT), USD Coin (USDC), and DAI collectively represent a significant portion of the crypto market capitalization.
Every Peg Has Its Day of Depeg
Despite their intended stability, stablecoins are susceptible to "depegging"—a scenario where their value diverges from the pegged fiat currency.
TerraUSD (UST) stands as one of the most striking examples of the colossal damage a depeg can inflict on financial markets. Its collapse in May 2022 wiped out nearly $40 billion in market capitalization and triggered a cascading series of failures across the crypto industry and beyond. The incident shattered confidence in algorithmic stablecoins, contributed to the downfall of major players like Celsius and Three Arrows Capital, and the ecosystem has not recovered since..
But even brief depegs can sow panic. In March 2023, USDC fell as low as $0.87 after its issuer, Circle, revealed a $3.3 billion exposure to the collapsed Silicon Valley Bank (SVB). The depeg lasted less than 48 hours, but it erased over $10 billion in market capitalization in days, dropping from around $43 billion to $32 billion before stabilizing.
DAI has also faced depeg events stemming from its reliance on USDC, notably in August 2022, when concerns arose that USDC held in MakerDAO’s Peg Stability Module (PSM) could be blacklisted due to regulatory action. The trigger was Circle’s freezing of over 75,000 USDC linked to Tornado Cash after the U.S. Treasury sanctioned the protocol. This raised fears that DAI’s USDC reserves—held in smart contracts—could be tainted or subject to censorship. DAI briefly fell to $0.97 as investors questioned the resilience of a decentralized stablecoin heavily backed by a centralized asset vulnerable to compliance risk. The event sparked internal debate at MakerDAO and intensified efforts to diversify DAI's collateral base and reduce reliance on USDC.
To mitigate depeg risks, stablecoin issuers employ various mechanisms such as backing each stablecoin with an equivalent amount of fiat currency, overcollateralization with cryptocurrencies and others.
However, these mechanisms are not foolproof, and the market lacks standardized tools for hedging against depeg events. This gap underscores the demand for independent products that allow users to manage depeg risks effectively.
Cork Against Stablecoin Depegs
Launched in 2024, the Cork Protocol is a DeFi platform designed to tokenize and trade the risk of stablecoin and liquid staking token depegging. By introducing Depeg Swaps (DS) and Cover Tokens (CT), Cork enables users to hedge against or earn from the stability of pegged assets.
Cork's innovation lies in its ability to create a permissionless, fully collateralized market for depeg risk, that operates contracts similar to call and put options in traditional finance.
At the heart of Cork Protocol is the Peg Stability Module (PSM), which facilitates the creation of DS and CT tokens:
- Depeg Swaps (DS): Functionally similar to put options, DS tokens grant holders the right to exchange a pegged asset for a redemption asset at a 1:1 ratio if a depeg occurs. For example, in an ETH::stETH market, a DS allows the holder to swap stETH for ETH if stETH depegs.
- Cover Tokens (CT): Analogous to call options, CT holders earn a fixed yield as long as the pegged asset maintains its peg. They effectively underwrite the depeg risk, receiving premiums from DS buyers.
The pricing of DS and CT tokens is influenced by market perceptions of depeg risk, time to maturity, and the volatility of the underlying assets. These tokens are tradable on secondary markets, providing liquidity and enabling dynamic risk management.
For example, if the market grows wary of a potential depeg, the demand for DS tokens increases—traders are now willing to pay more for protection. This spike in demand drives up the price of DS tokens.
At the same time, this rising price creates an incentive for new liquidity providers to mint DS and CT tokens by depositing collateral into the Cork Peg Stability Module. Their participation brings fresh capital into the system and restores liquidity to the DS/CT market.
Cork Protocol Idea and Implementation
Cork Protocol emerged from the a16z Crypto Startup Accelerator, securing investment from Andreessen Horowitz (a16z) in 2024.
Cork Protocol has established several strategic partnerships within the DeFi ecosystem to broaden its market offerings and integrate its risk management tools across platforms. Notable collaborations include the stablecoin protocols Ethena, Sky (formerly associated with MakerDAO's DAI), and Resolv, as well as liquid staking providers Lido and EtherFi.
Cork’s integration with platforms like Uniswap V4 has further enhanced its visibility and adoption. By leveraging Uniswap’s advanced features, Cork offers more efficient and customizable risk management solutions. This enables dynamic pricing and improved liquidity for DS and CT tokens, making it easier for users to manage exposure to depeg events.
These developments have helped the protocol reach over $30 million in total value locked (TVL) in its Peg Stability Module.
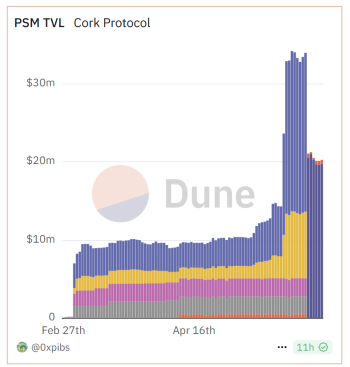
On May 28, 2025, Cork Protocol suffered a significant exploit resulting in the loss of approximately $12 million in wrapped staked ETH (wstETH).
The attacker exploited vulnerabilities in the protocol's smart contracts, specifically, created markets with arbitrary redemption assets without proper validation, made possible by a lack of access controls in one of its functions.
By manipulating these flaws, the attacker created a fake market, minted illegitimate DS and CT tokens, and redeemed them for real assets, effectively draining liquidity from the legitimate market.
Nevertheless, Cork Protocol offers a unique approach to depeg risk management, and the project will likely recover from the incident and continue its development. Added to our Observation list.

